IntraOpVSP
Intra operative virtual surgical planning using AR and Computer Vision.
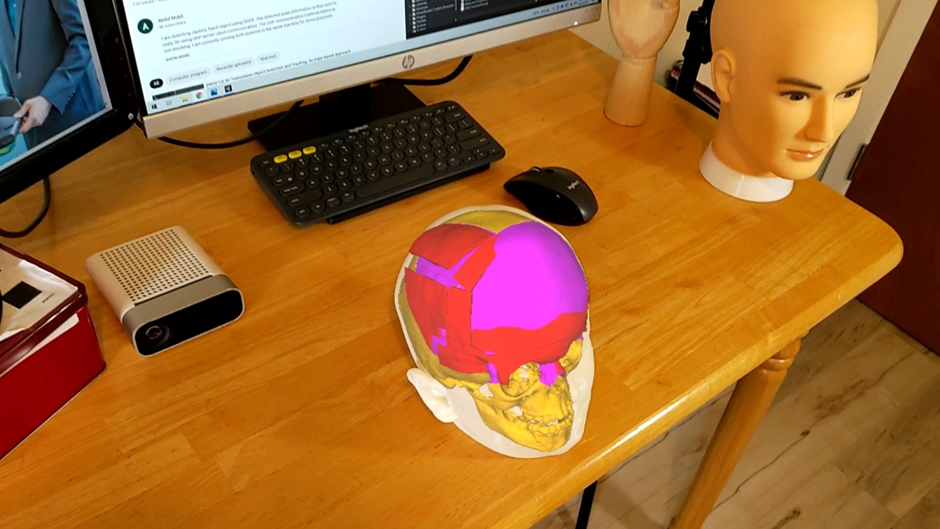
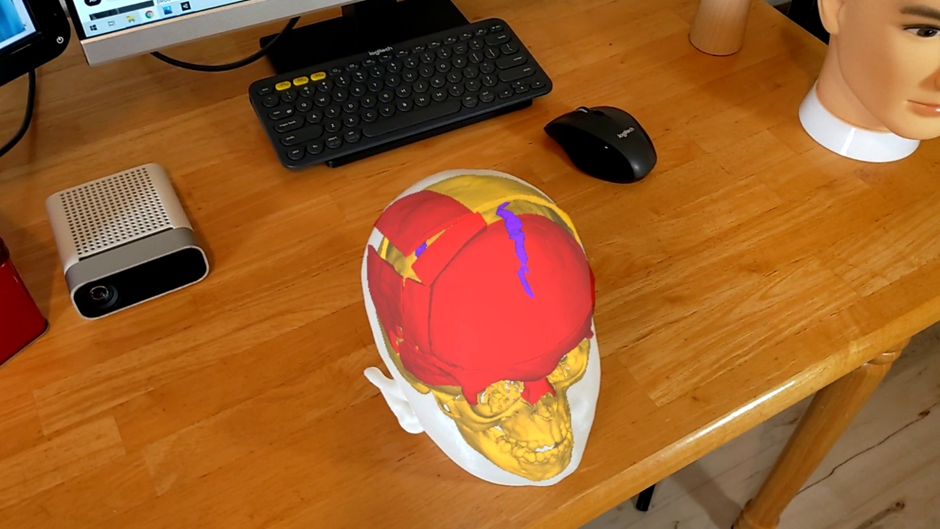
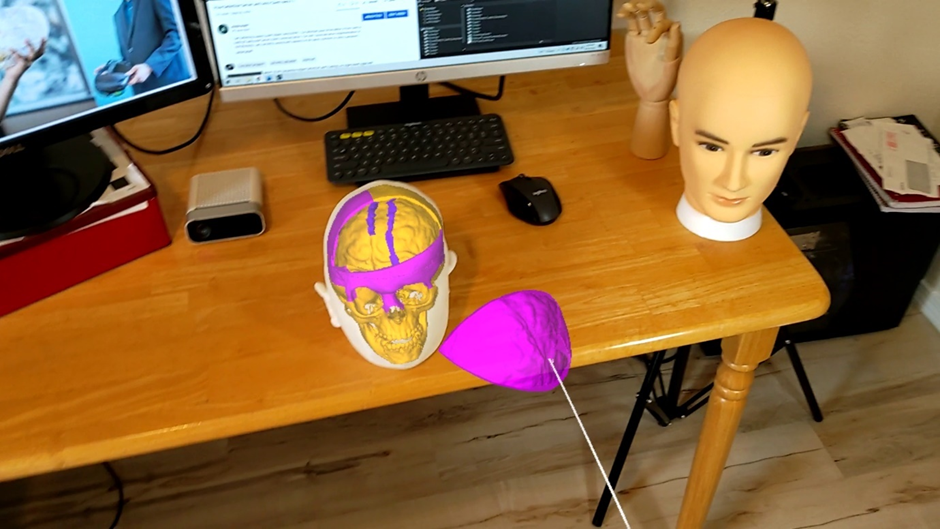
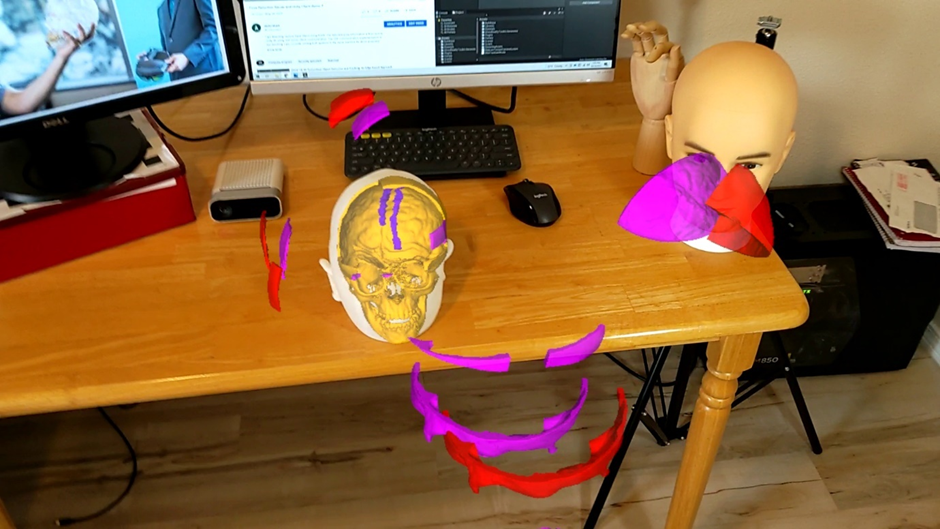
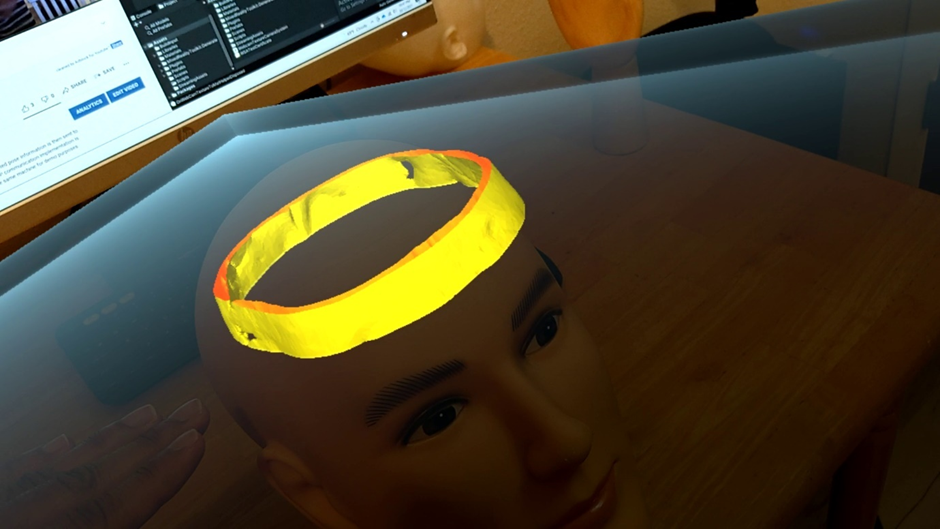
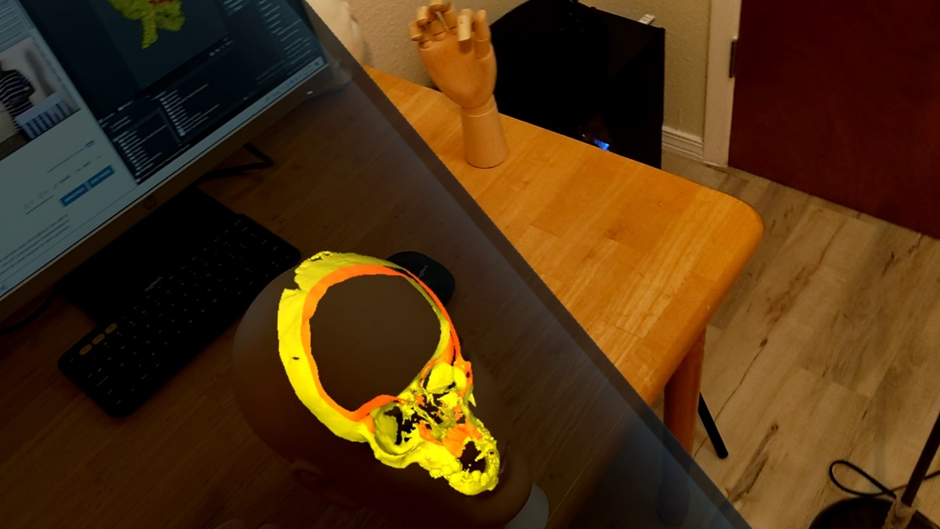
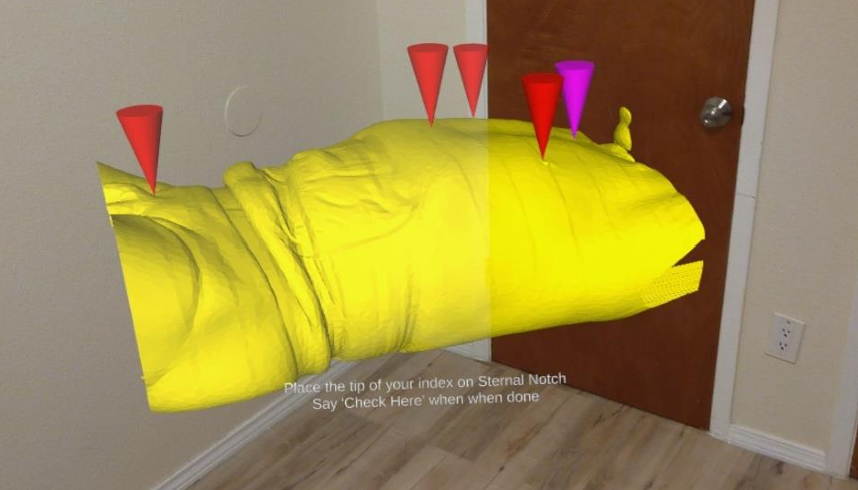
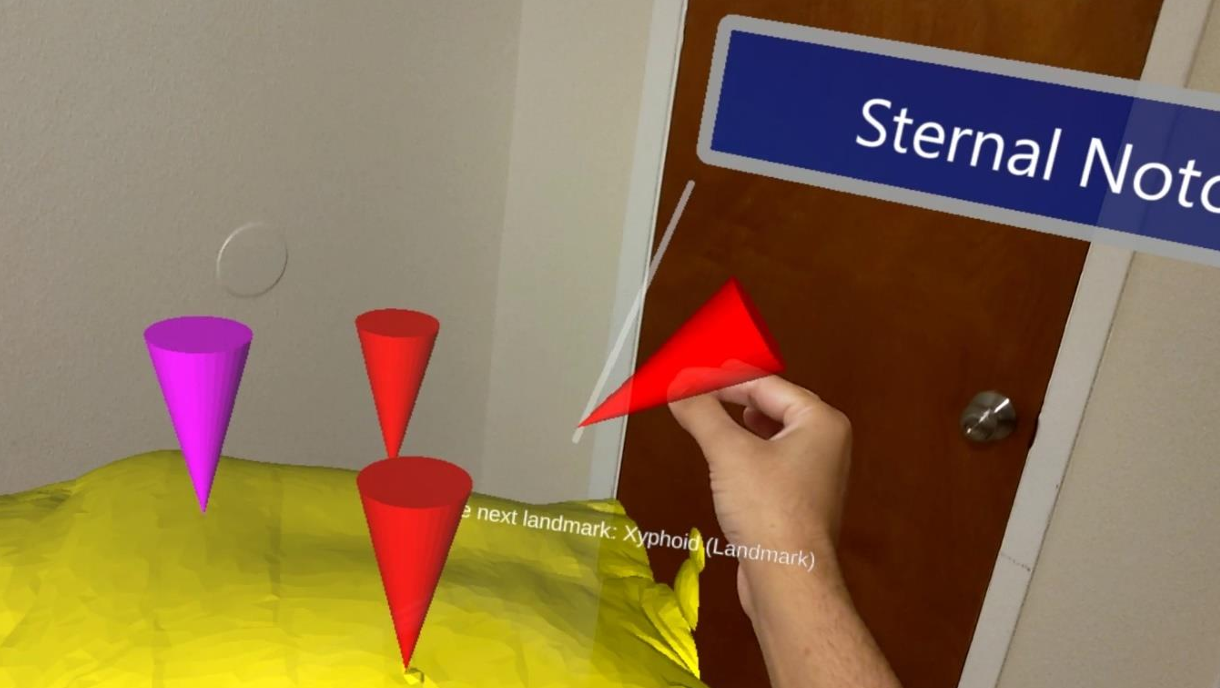
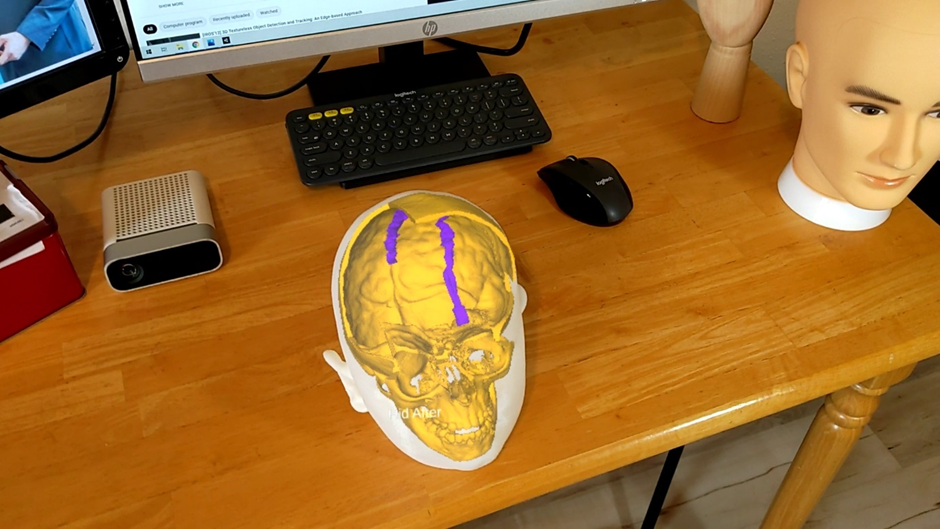
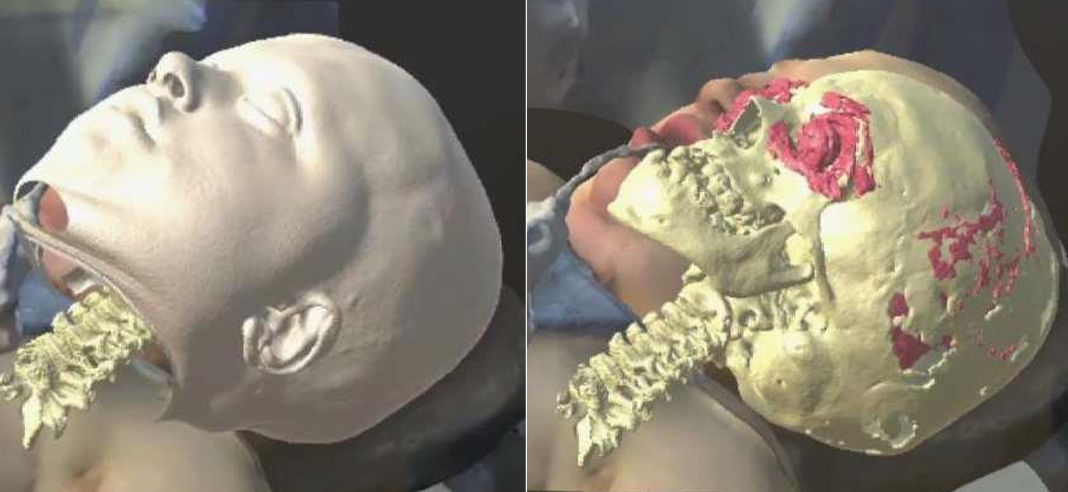
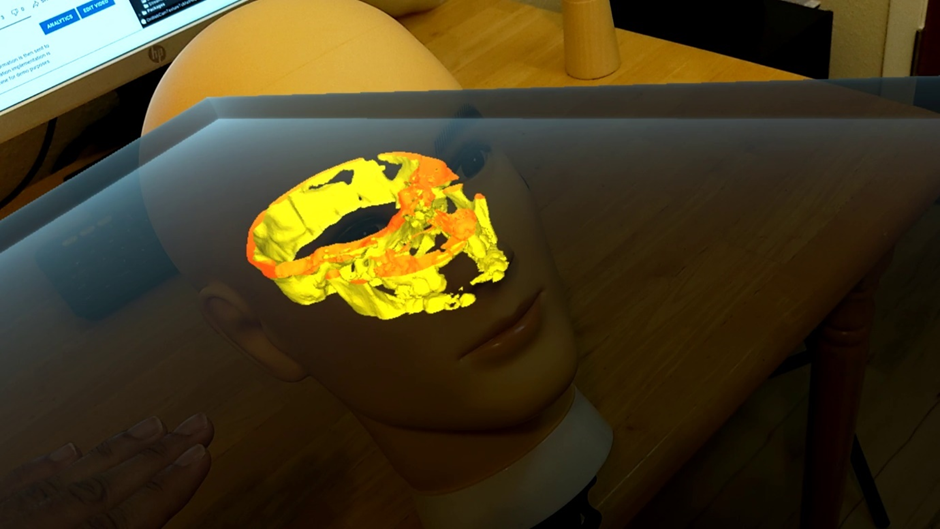
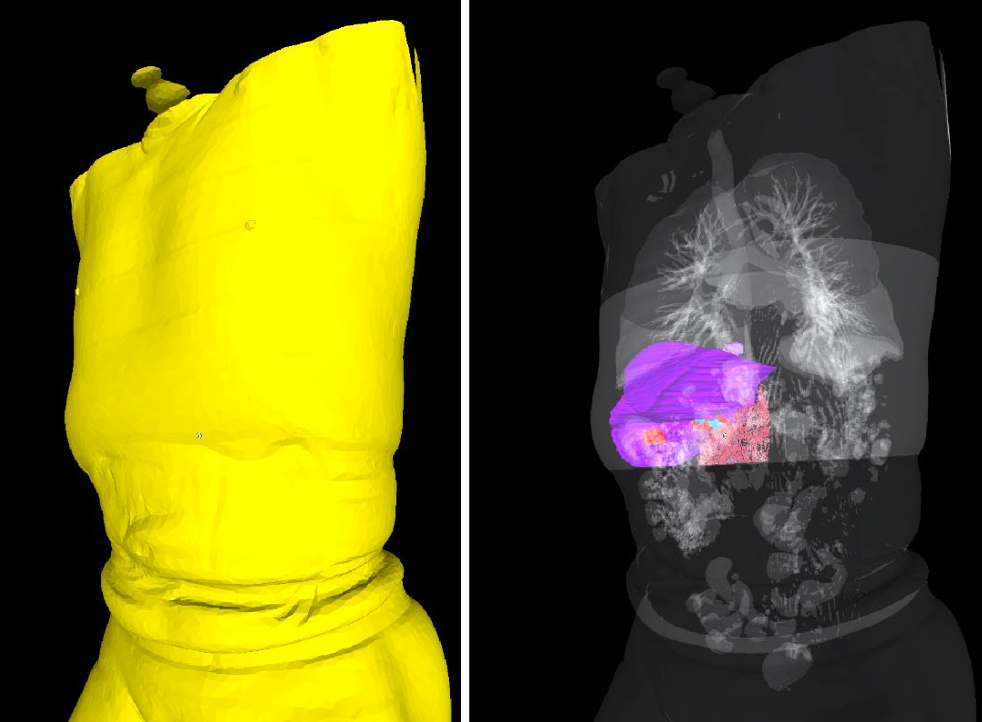
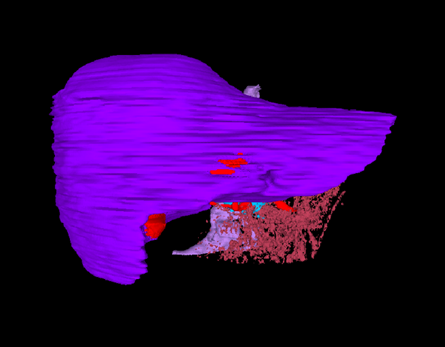
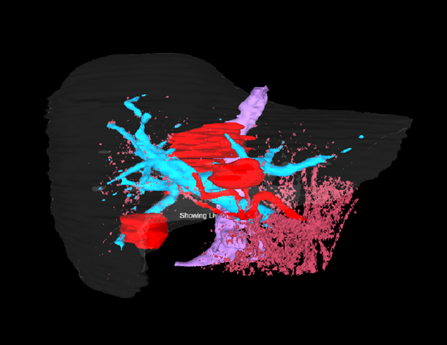
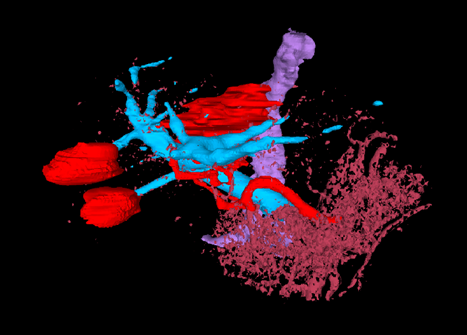
A set of mixed-reality apps that allow surgeons to anatomically align and interact with CT scan data through Microsoft Hololens. The technology has been used in over 50 human surgeries. The technology has been licensed to a startup for commercialization and has been approved by FDA.
My Contributions
As part of my MS research, I implemented the technology from scratch.
- Developed mixed reality software using Unity, Mixed Reality Toolkit, and Microsoft Hololens-2.
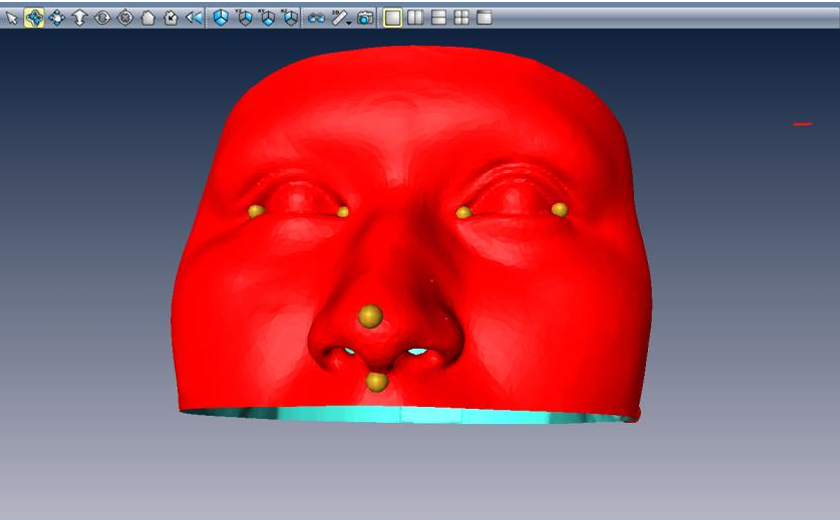
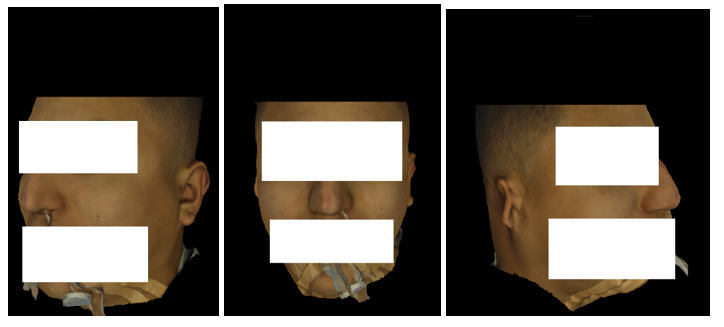
- Used OpenCV, DLib, and PyTorch for 6-DoF pose estimation of human head and surgical tools.
- Annotated 2D, 3D data for machine learning.
Skills/Tools: PyTorch, OpenCV, Unity3D, Blender, MeshLab, DLib, C++, C#, Python.
The Problem
The mission is to augment every surgery. Compared to a pilot flying a plane or even a regular google-map user on his way to work/home, surgeons today have their instruments clustered behind them hanging in the wall. The Google Maps user or the pilot gets constant real-time updates regarding where they are, what to do next, and other vital data that helps them make split-second decisions. They don’t have to plan the trip for days or memorize every turn and detail of every landmark along the way. They just do it. On the other hand, surgeons today have to do rigorous surgical planning, memorize the specifics of each unique case, and all the necessary steps to ensure the safest possible surgery. Then they engage in complex procedures for several hours, with no targeting or homing devices or head-mounted displays to assist them. They have to feel their way to their objective and hope everything goes as they planned. In my research, I made the “google-maps” for surgery.
Examples:
Following are IntraOpVSP usage examples: